Remember that high school chemistry class when your teacher introduced the concepts of acids and bases? Do you recall the confusion, the struggle to understand the difference between acidic and basic solutions, and the daunting equations that seemed to defy all logic? Well, fear not! This article will delve deep into the fascinating world of acids and bases, providing not only a thorough understanding of the fundamentals but also offering you a valuable resource: a comprehensive worksheet with answers PDF.
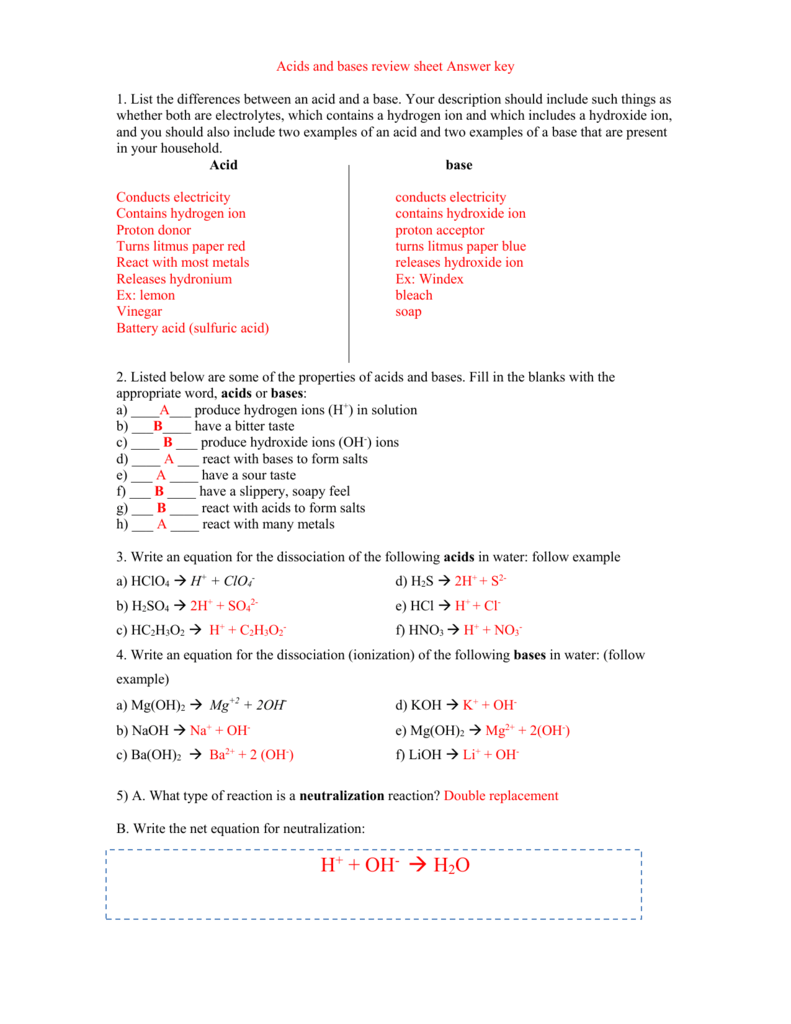
Image: wordworksheet.com
Let’s embark on a journey to conquer the topic of acids and bases. Our guide? This detailed article that will demystify the concepts behind acids and bases. By the end of this reading, not only will you be comfortable with the definitions, properties, and reactions involving acids and bases, but you will also have access to a readily available worksheet with answers, putting you on the fast track to mastering these chemical concepts. So, let’s get started!
Understanding Acids and Bases: A Fundamental Guide
Acids and bases are fundamental concepts in chemistry, laying the groundwork for understanding a wide range of chemical reactions and processes. From the sour taste of lemons to the slippery feel of soap, the presence of acids and bases permeates our everyday lives.
But what exactly are acids and bases? How do they interact and what makes them so important? Simply put, acids and bases are two categories of substances that exhibit specific properties, primarily their ability to donate or accept protons (hydrogen ions, H+). These properties have profound implications in various fields, from medicine and agriculture to environmental science and industrial processes.
Defining Acids and Bases: Two Major Theories
The idea of acids and bases has evolved over time, leading to various theoretical frameworks to describe their behavior. Two major theories that have shaped our understanding are the Arrhenius theory and the Brønsted-Lowry theory.
The Arrhenius Theory: A Historical Perspective
Svante Arrhenius, a Swedish chemist, proposed the Arrhenius theory in 1884. He defined acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases were defined as substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) is considered an Arrhenius acid because it ionizes in water to form H+ and Cl-. Similarly, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is an Arrhenius base because it dissociates into Na+ and OH- ions in water. The Arrhenius theory provided a crucial framework for understanding acids and bases, but it had limitations in explaining the behavior of some substances that did not fit neatly into these definitions.
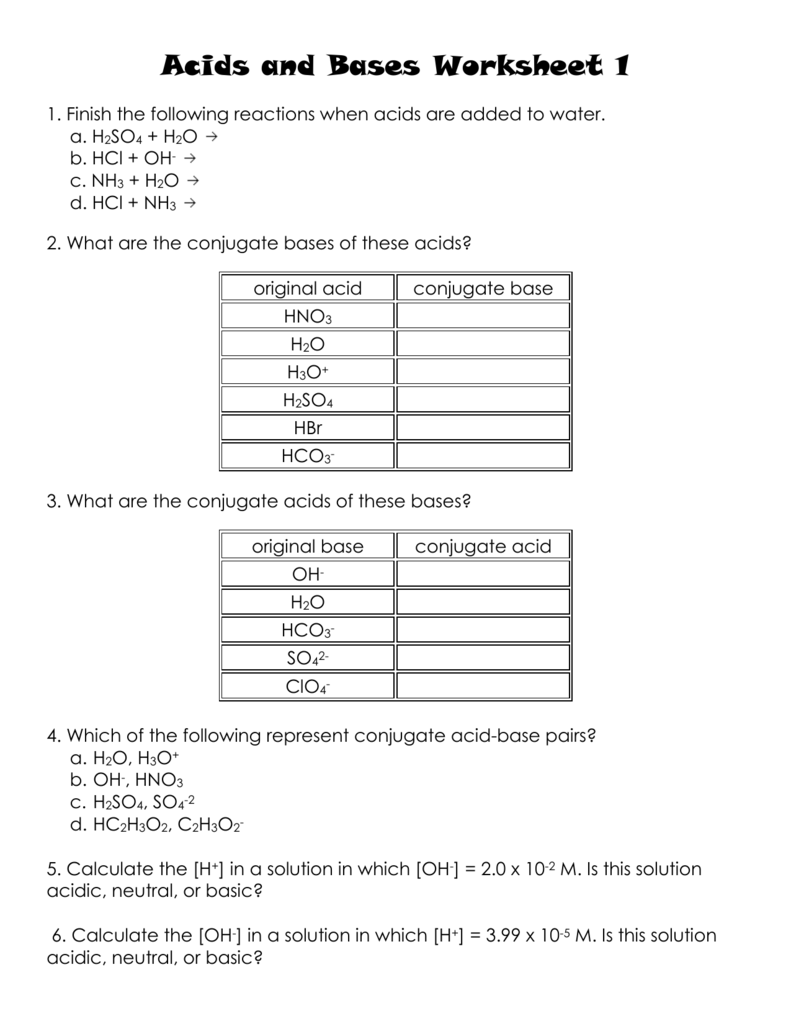
Image: worksheetlibraryjunker.z13.web.core.windows.net
The Brønsted-Lowry Theory: A Broader Definition
In 1923, Johannes Brønsted and Thomas Lowry independently proposed a more general definition of acids and bases. The Brønsted-Lowry theory expanded the scope beyond aqueous solutions, focusing on the transfer of protons (H+) in chemical reactions.
According to this theory, an acid is a substance that can donate a proton (H+) to another substance, and a base is a substance that can accept a proton. This broader definition encompasses a wider range of substances, including those that do not necessarily contain hydrogen or hydroxide ions. For example, ammonia (NH3) is a Brønsted-Lowry base because it can accept a proton from an acid, forming the ammonium ion (NH4+).
The pH Scale: Measuring the Strength of Acids and Bases
One of the most common ways to express the acidity or basicity of a solution is using the pH scale. The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 representing a neutral solution. Values below 7 indicate acidic solutions, while values above 7 represent basic solutions. The lower the pH value, the more acidic the solution. Conversely, the higher the pH value, the more basic the solution.
The pH scale is based on the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. It’s important to note that the pH scale is not linear; each change of one unit on the pH scale represents a tenfold change in the concentration of H+ ions. Therefore, a solution with a pH of 4 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 5 and one hundred times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 6.
Key Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases exhibit characteristic properties that are central to their behavior and applications. Here are some of the key properties to remember:
Acids
- Sour taste: Acids have a characteristic sour taste. For example, the sour taste of citrus fruits is due to the presence of citric acid.
- Reacts with metals to produce hydrogen gas: Acids react with certain metals (such as zinc, magnesium, and iron) to generate hydrogen gas. This reaction is often used to test for the presence of an acid.
- Turns blue litmus paper red: Litmus paper is a pH indicator that changes color depending on the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
- Reacts with bases to form salts and water: Acids react with bases in a neutralization reaction, producing salt and water.
Bases
- Bitter taste: Bases typically have a bitter taste. For instance, the bitterness of soap is attributed to the presence of bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Slippery feel: Bases feel slippery to the touch, a property often associated with soaps and detergents. This is because bases react with fats and oils to form soap-like substances.
- Turns red litmus paper blue: Just as acids change blue litmus paper red, bases have the opposite effect, turning red litmus paper blue.
- Reacts with acids to form salts and water: Similar to acids, bases react with acids to produce salts and water in a neutralization reaction.
Examples of Acids and Bases: Everyday Encounters
Acids and bases are not just concepts found in textbooks; they play significant roles in our everyday lives. Here are some common examples of acids and bases you may encounter:
Acids
- Vinegar: Contains acetic acid, which gives vinegar its sour taste and is used in cooking, cleaning, and preserving.
- Citric acid: Found in citrus fruits, it is responsible for their sour taste and is often used in food and beverages.
- Lactic acid: Produced by bacteria in milk, it is responsible for the sour taste of yogurt and is associated with muscle fatigue during exercise.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl): A strong acid, it is found in gastric juices and plays a crucial role in digestion.
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4): A highly corrosive acid, it is used in battery production and various industrial processes.
Bases
- Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate): A mild base, it is commonly used in baking, cleaning, and as an antacid.
- Soap: A mixture of fatty acids and bases, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). It is used for cleaning and personal hygiene.
- Ammonia (NH3): A common base used in household cleaning products, it is also used in the production of fertilizers and explosives.
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): A strong base, also known as lye, it is used in soap making, paper production, and drain cleaning.
- Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2): A strong base, also known as slaked lime, it is used in construction, agriculture, and water treatment.
Acids and Bases Worksheet with Answers PDF: Your Study Companion
To reinforce your understanding of acids and bases, I’ve created a comprehensive worksheet with answers PDF that covers various topics, ranging from definitions to reactions, and includes additional practice questions. The worksheet will help you:
- Strengthen your comprehension: The worksheet provides numerous examples and exercises that will help you solidify your understanding of the key concepts related to acids and bases.
- Master the terminology: By working through the worksheet, you’ll become familiar with the terminology used in acid-base chemistry, ensuring you can communicate effectively about these concepts.
- Develop problem-solving skills: The worksheet includes a variety of problem sets that will challenge you to apply your knowledge and enhance your critical thinking skills.
- Practice for exams: The worksheet can be a valuable resource to prepare for any upcoming exams, quizzes, or tests on acids and bases.
The worksheet with answers PDF is available for free download, giving you convenient access to a valuable study tool. You can use it independently or as a supplement to your classroom learning. Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you engage with the material through the worksheet and related exercises, the greater your understanding will become.
Tips and Expert Advice: Mastering Acids and Bases
Here’s some expert advice and tips for achieving mastery in the realm of acids and bases:
- Visualize the Concepts: Instead of just memorizing definitions, focus on creating mental images to understand the process of proton donation or acceptance in acids and bases. This approach enhances comprehension and retention.
- Practice with Examples: Utilize real-world examples of acids and bases to make the concepts more relatable. For instance, consider how the sourness of citrus fruits is related to the presence of citric acid or how baking soda’s ability to neutralize acids is crucial in baking.
- Engage in Active Learning: Instead of simply passively reading through textbooks, engage in active learning techniques. This could involve summarizing information in your own words, creating flashcards, or discussing acid-base concepts with peers.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask Questions: If you encounter any confusion or have questions, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher, tutor, or fellow students. Clear communication is key to effectively addressing any knowledge gaps and ensuring a solid grasp of the concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
A: The strength of an acid refers to its ability to donate protons (H+). A strong acid like hydrochloric acid (HCl) completely ionizes in water, meaning it releases all its protons, forming H+ and Cl- ions. On the other hand, a weak acid like acetic acid (CH3COOH) only partially ionizes in water. It only releases a small portion of its protons, maintaining a balance between the undissociated and ionized forms.
Q: What is the difference between a strong base and a weak base?
A: Similar to acids, the strength of a base reflects its ability to accept protons (H+). A strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) completely dissociates in water, generating hydroxide ions (OH-) and sodium ions (Na+). In contrast, a weak base like ammonia (NH3) only partially accepts protons, maintaining a balance between the free base molecules and the protonated form (NH4+).
Q: What is a pH indicator?
A: A pH indicator is a substance that changes color depending on the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is a visual tool to determine the pH range of a solution. Litmus paper is a common example of a pH indicator; it turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions.
Q: How do acids and bases affect the environment?
A: Acids and bases can have significant effects on the environment. Acid rain, caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from burning fossil fuels, can harm forests, lakes, and aquatic life. Similarly, industrial waste containing acids and bases can pollute water sources, impacting ecosystems and human health.
Q: How are acids and bases used in our daily lives?
A: Acids and bases have numerous applications in daily life. Acids are used in food production, pharmaceutical industries, and as cleaning agents. Bases are essential for soap and detergent making, various industrial processes, and as components in fertilizers.
Acids And Bases Worksheet With Answers Pdf
Conclusion
Understanding acids and bases is essential for anyone interested in chemistry, biology, or related sciences. These concepts are fundamental to numerous chemical reactions and processes, impacting our lives in countless ways. By grasping the definitions, properties, and reactions associated with acids and bases, you can develop a sound foundation for exploring more advanced chemistry topics. Utilizing this comprehensive worksheet with answers PDF will help you reinforce your knowledge and become confident in your understanding of acids and bases.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the world of acids and bases? Let’s discuss and gain further understanding from this resource. Share any questions or thoughts about this topic in the comments section below!






