Ever had the frustration of a dead headlight on your 2011 Dodge Nitro, only to find yourself staring at a bewildering array of fuses in the fuse box? You’re not alone. For many Nitro owners, the fuse box can seem like a cryptic puzzle, but understanding its layout and functions can save you time, money, and a whole lot of frustration. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the 2011 Dodge Nitro fuse box with confidence, enabling you to diagnose and resolve electrical issues yourself.
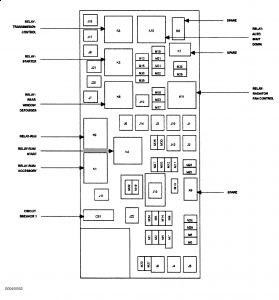
Image: diagramdbgregg.z22.web.core.windows.net
The fuse box, often referred to as the “fuse panel,” is the central hub of your Nitro’s electrical system. It safeguards your vehicle by protecting its electrical components from overloads and shorts. Each fuse is like a small soldier, sacrificing itself to prevent a larger fire or malfunction within your system. With the right information and a little troubleshooting, you can identify and replace blown fuses, restoring your Nitro’s functionality in a snap. So, let’s dive into the world of fuses and unlock the secrets of your 2011 Dodge Nitro fuse box.
The Importance of the Fuse Box
Imagine a complex network of electrical pathways throughout your Nitro, powering everything from the headlights and taillights to the radio and air conditioning. Each of these components is susceptible to electrical faults. Without a fuse box, a minor short in one circuit could potentially cascade, damaging multiple systems and crippling your vehicle. This is where the fuse box steps in as the guardian of your Nitro’s electrical well-being.
Understanding Fuse Types and Their Uses
Fuses are essentially sacrificial devices designed to break a circuit before excessive current can damage expensive components. Each fuse is rated for a specific amperage, signifying the maximum amount of current it can safely conduct. If the current exceeds that rating, the fuse melts, interrupting the flow of electricity.
Think of it like this: imagine a thin wire, like a fuse, is carrying electricity to your headlights. If there’s a short circuit or overload, the current will spike. This increased flow of electricity will heat up the wire. If the wire isn’t strong enough to handle the extra heat, it’ll melt, breaking the circuit before any damage is done to your headlights.
Types of Fuses:
- Standard blade fuses: These are the most common type and have a simple blade design that inserts into dedicated slots within the fuse box.
- Mini blade fuses: Similar to standard blade fuses but slightly smaller, these are often found in newer vehicles.
- ATO (Automotive Terminal Output) fuses: They have a slightly larger body but still use the same blade design.
- ATC (Automotive Terminal Circuit) fuses: Another popular type, ATC fuses are slightly smaller than ATO fuses.
![[DIAGRAM] 2007 Dodge Nitro 37 Relay Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://f01.justanswer.com/ebrock63/eca7be91-4086-4925-95d9-512b10191685_2015-09-30_155751.png)
Image: mydiagram.online
Locating the Fuse Box(es) in Your 2011 Dodge Nitro
Your 2011 Dodge Nitro has multiple fuse boxes, strategically placed to accommodate the various circuits and components in your vehicle. Let’s explore these key locations:
1. Under the Hood Fuse Box:
This fuse box is typically located on the driver’s side of the engine compartment, near the battery. It houses fuses for many essential functions, including the engine, lights, and accessories.
2. Interior Fuse Box:
This fuse box is usually located on the driver’s side of the dashboard, either beneath the steering wheel or in a dedicated compartment. This box typically protects circuits related to your interior lighting, power accessories, and some dashboard-mounted controls.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to understanding the layout and function of each fuse. It’s essential for troubleshooting electrical issues. Here’s how to interpret the diagram:
- Fuse Numbers: Each fuse has a unique number, making it easy to identify.
- Amperage Rating: The diagram will show the amperage rating of each fuse, indicating its current-carrying capacity.
- Component Descriptions: The diagram will list the electrical components that each fuse protects. For example, a fuse may be labeled “Headlights,” “Radio,” or “Power Windows.”
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues with Your Fuse Box
When an electrical component malfunctions or stops working, the first step is to check the corresponding fuse for signs of damage. A blown fuse will often be visually identifiable, with a melted or broken wire. Here’s how to approach the troubleshooting process:
- Locate the Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to determine which fuse corresponds to the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully inspect the fuse, looking for any signs of melting, breakage, or discoloration. If you see any of these signs, it’s likely that the fuse has blown.
- Replace the Fuse: If you’ve confirmed that the fuse is blown, it’s time to replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never replace a blown fuse with a higher-amperage fuse, as this can damage your electrical system.
- Investigate the Root Cause: After replacing the blown fuse, if the component still doesn’t work, the issue might lie deeper than the fuse itself. There could be a short circuit or other electrical fault that needs to be addressed. It’s best to consult a qualified mechanic in this case.
Safety Precautions
Working with electricity can be dangerous. Always take necessary precautions to prevent injury or damage to your vehicle:
- Never work on electrical components with the engine running. Turn off the ignition and disconnect the negative battery terminal before working in the fuse boxes.
- Be careful not to touch any exposed metal parts in the fuse box or electrical system.
- Always use fuses with the correct amperage rating. Never replace a fuse with one that has a higher amperage rating.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of the process, consult a qualified mechanic.
Tips for Maintaining Your Fuse Box
Regular maintenance of your fuse box can help prevent electrical problems and keep your Nitro running smoothly:
- Inspect the fuse box periodically for corrosion or damage. Clean any corrosion with a wire brush or a solution designed for this purpose.
- Avoid overloading the electrical system by using excessive accessories or high-wattage devices.
- Replace any worn or damaged fuses promptly. A blown fuse is a signal that there might be a deeper issue, so investigate the root cause to prevent future problems.
2011 Dodge Nitro Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion
Understanding the layout, function, and troubleshooting techniques of your 2011 Dodge Nitro fuse box empowers you to deal with minor electrical issues efficiently and prevent bigger problems down the road. With this comprehensive guide, you can confidently tackle those burnt-out headlights, faulty radio signals, or any other electrical gremlins that might pop up. Remember, electrical systems are complex, so if you ever encounter an issue you can’t address yourself, don’t hesitate to seek help from a skilled mechanic.






