Have you ever found yourself staring at a serpentine belt diagram, feeling like you’re looking at hieroglyphics? It can be intimidating, especially when your car’s engine is making those ominous screeching noises, and you’re trying to figure out what’s wrong. But fear not! In this article, we’ll break down the 2012 Chevy Traverse serpentine belt diagram, unraveling the mysteries of this vital engine component. We’ll walk you through its components, routing, and provide helpful tips for navigating this seemingly complex system.

Image: fixenginejack99.z19.web.core.windows.net
The 2012 Chevy Traverse, like many modern vehicles, relies on a single belt to power various essential systems, including the power steering pump, alternator, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. This serpentine belt acts like a central artery, transmitting power from the engine to these crucial components. Understanding the configuration of this belt is key to diagnosing potential issues and ensuring your Traverse runs smoothly.
Understanding the 2012 Chevy Traverse Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram for the 2012 Chevy Traverse is a visual representation of how the belt runs throughout the engine, highlighting the specific components it drives. It’s essentially a roadmap for understanding the belt’s route and identifying any potential problems.
Let’s break down the essential components and their roles within the serpentine belt system:
Serpentine Belt
This is the main component, a rubber belt with a ribbed surface for increased grip and power transmission. It’s crucial for providing power to the various engine accessories it drives.
Crankshaft Pulley
This pulley is attached to the crankshaft, the rotating element that converts reciprocating motion to rotary motion in the engine. It acts as the starting point for the serpentine belt’s journey.
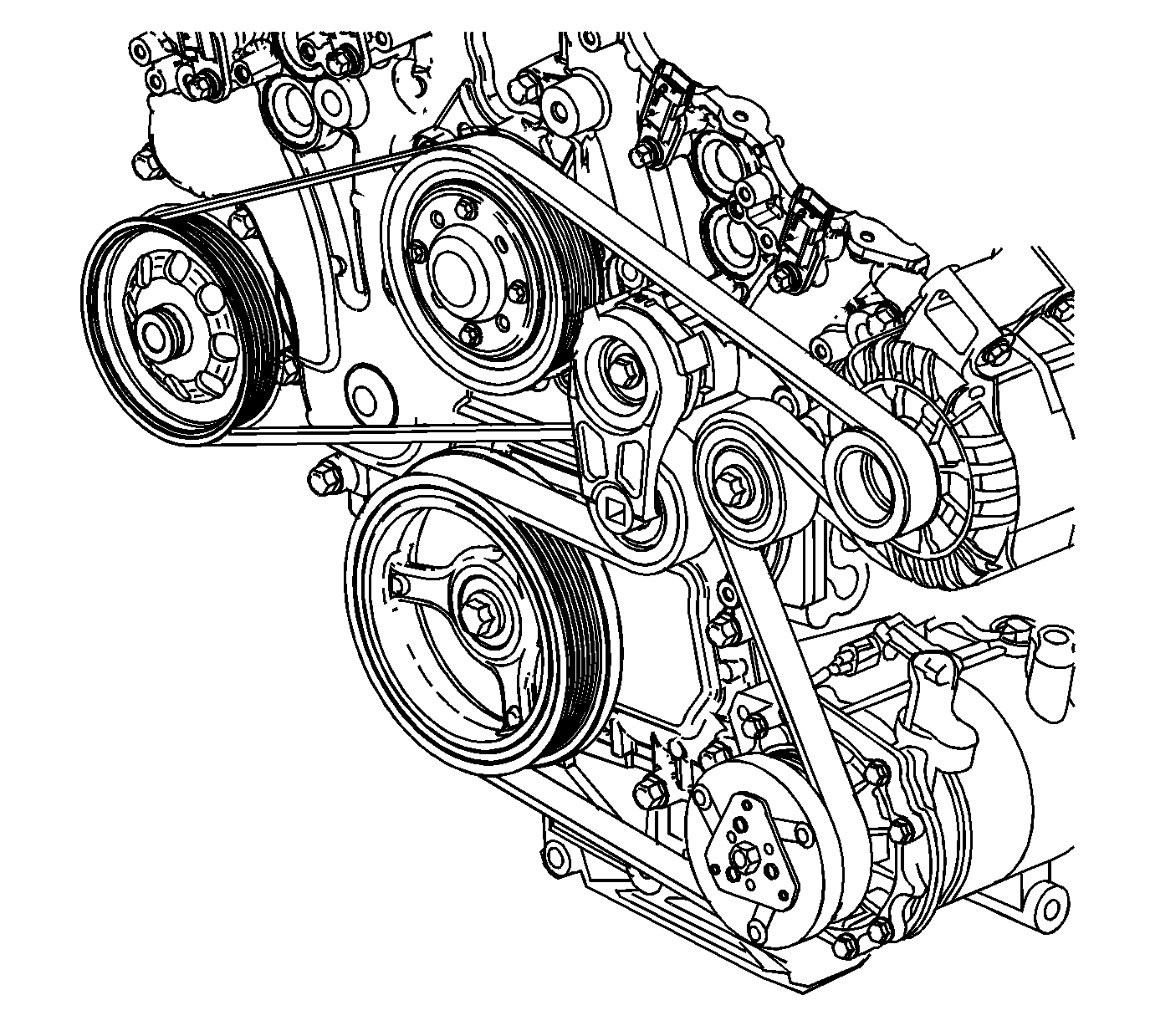
Image: tourback.blogspot.com
Power Steering Pump
This pump is responsible for providing hydraulic pressure to the steering system, making it easier to turn the wheel. The serpentine belt drives the power steering pump, ensuring smooth and responsive steering.
Alternator
The alternator generates electrical energy for charging the battery and powering the car’s electrical system. The serpentine belt spins the alternator, keeping the battery topped up and ensuring proper operation of all electrical components.
Air Conditioning Compressor
This compressor pumps refrigerant through the air conditioning system, providing cooling air inside the car. The serpentine belt drives the compressor to enable climate control.
Water Pump
This pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, preventing overheating. The serpentine belt drives the water pump, maintaining optimal engine temperature.
Serpentine Belt Tensioner
This component adjusts belt tension, ensuring proper engagement and preventing slipping or premature wear. The tensioner is crucial for maintaining belt performance.
The Importance of a Properly Functioning Serpentine Belt
Imagine your Traverse’s engine as a well-oiled machine, and the serpentine belt is the oil that keeps everything moving smoothly. A properly functioning serpentine belt is essential for:
- Power Steering Functionality: If the serpentine belt fails, you’ll lose power steering, making your vehicle extremely difficult to maneuver.
- Engine Cooling: Without a properly functioning water pump, driven by the serpentine belt, your engine could overheat, leading to costly repairs.
- Electrical System Performance: A damaged serpentine belt can prevent the alternator from charging the battery, leaving you stranded with a dead battery.
- Climate Control: A broken belt disables the air conditioning compressor, meaning no cool air for those hot summer days.
Common Serpentine Belt Problems
While serpentine belts are generally designed to be durable, they can still suffer from wear and tear over time. Here are some common problems that can arise:
- Belt Wear and Tear: Repeated use and exposure to environmental factors can result in cracks, fraying, and weakening of the belt.
- Belt Slipping: Loss of tension can cause the belt to slip, resulting in a characteristic screeching noise and a decrease in accessory performance.
- Belt Breakage: Severe wear or improper tension can lead to belt breakage, causing a complete loss of accessory function.
Identifying Serpentine Belt Symptoms
If you suspect a problem with your serpentine belt, it’s important to identify the warning signs early to prevent more serious damage.
Common Serpentine Belt Symptoms:
- High-pitched squealing or screeching noise coming from the engine, especially when accelerating or turning the steering wheel.
- Stiff or sluggish steering, indicating a failing power steering pump.
- Battery light flashing or indicating a low charge.
- Air conditioning not working properly.
- Engine overheating.
Expert Tips
Being proactive is key to avoiding serpentine belt issues and keeping your Traverse running smoothly. Here are some expert tips for maintaining your belt:
Tips for Serpentine Belt Maintenance:
- Regular Visual Inspections: Inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or any signs of wear.
- Check Belt Tension: Use a tension gauge to ensure the belt has the correct tension. Proper tension prevents slipping and premature wear.
- Replace Worn Belts: Don’t wait until the belt breaks! Replace it if you see signs of wear or if it’s approaching its recommended replacement interval.
- Avoid Using Oil-Based Fluids: Keep oil, grease, and other fluids away from the belt, as these can degrade the rubber and shorten its lifespan.
FAQs About the 2012 Chevy Traverse Serpentine Belt
Q. How often should I replace the serpentine belt?
A. General recommendations for serpentine belt replacement vary but are often around 60,000 to 100,000 miles. The specific interval may depend on driving conditions and your vehicle’s maintenance schedule. Check your owner’s manual for recommended replacement intervals.
Q. Can I replace the serpentine belt myself?
A. While some DIY-minded individuals might attempt a serpentine belt replacement, it’s advisable to have a mechanic perform the task. It involves specific tools and procedures to ensure proper tension and installation.
Q. What is the cost of replacing a serpentine belt?
A. The cost of replacing a serpentine belt can vary depending on the mechanic’s labor rates and the specific belt part. Generally, the cost for parts and labor could be anywhere from $100 to $300.
2012 Chevy Traverse Serpentine Belt Diagram
Conclusion
Understanding the 2012 Chevy Traverse serpentine belt diagram can save you a lot of headaches in the long run. By recognizing the signs of a failing belt, performing regular inspections, and following expert tips, you can keep your Traverse running smoothly and avoid costly repairs.
Are you interested in learning more about automotive maintenance or have any questions about the serpentine belt on your 2012 Chevy Traverse? Let us know in the comments below!






