Have you ever wondered how the concentration of reactants and products in a chemical reaction influences its equilibrium? It’s a fascinating concept that explains why some reactions favor the formation of products while others seem to barely react at all. I remember struggling with this concept when I first encountered it, but then I discovered the “Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo,” a virtual tool that brought the abstract ideas to life. This gizmo, through its interactive simulations, helped me grasp the intricate relationship between concentration and equilibrium in a way that textbooks alone couldn’t. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of equilibrium and concentration, exploring how the Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo can help you understand this important concept.
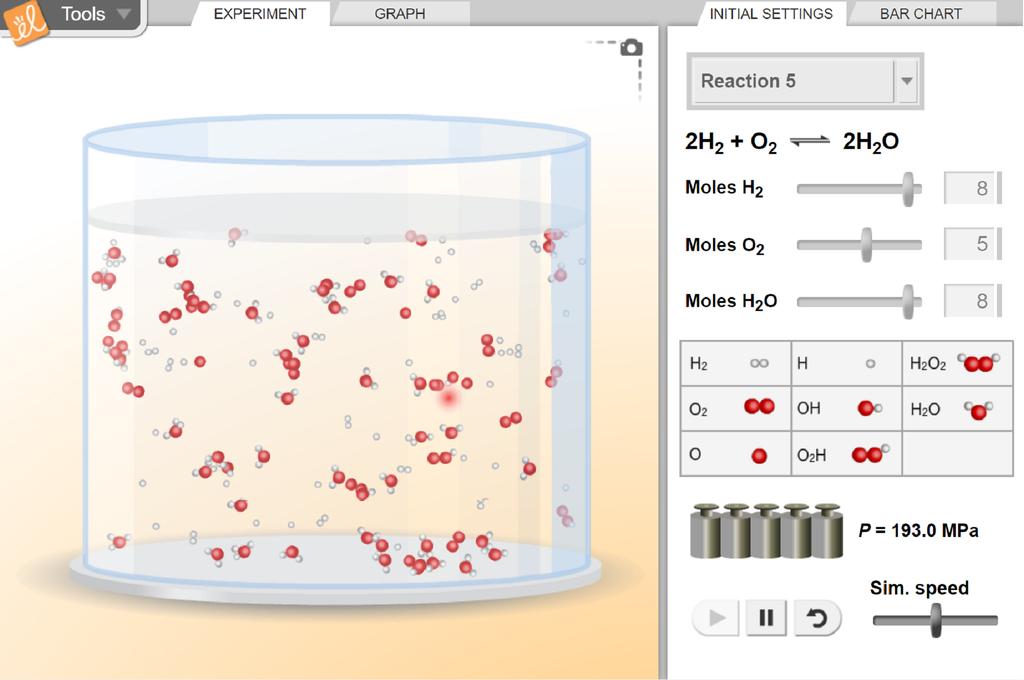
Image: gizmos.explorelearning.com
The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo is a powerful tool that allows users to explore the principles of chemical equilibrium, specifically how changing the concentration of reactants and products affects the position of equilibrium. Through interactive simulations, users can observe the dynamic interplay between forward and reverse reactions, resulting in a deeper understanding of the underlying principles.
The Equilibrium and Concentration Gizmo: A Virtual Laboratory for Chemical Reactions
The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo provides a virtual laboratory where users can conduct experiments and observe the effects of changing concentrations on chemical reactions in a safe and controlled environment. This gizmo allows you to manipulate variables like temperature, pressure, and concentrations of reactants and products, simulating real-world scenarios and enabling you to analyze the resulting shifts in equilibrium.
Understanding Chemical Equilibrium: A Balancing Act Between Forward and Reverse Reactions
Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. In simple terms, it means that the reactants are being converted into products at the same rate as products are being converted back into reactants. This state of balance is not static; it is a constant interplay between the forward and reverse reactions, where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time.
Le Chatelier’s Principle: Shifting Equilibrium with Concentration Changes
Le Chatelier’s principle, a fundamental concept in chemistry, states that if a change of condition is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that relieves the stress. When it comes to concentration changes, Le Chatelier’s principle predicts that if the concentration of a reactant is increased, the equilibrium will shift towards the products to consume the excess reactant. Conversely, if the concentration of a product is increased, the equilibrium will shift towards the reactants to reduce the excess product.

Image: bestans.heinrich-popow.com
The Equilibrium Constant: Quantifying Equilibrium
The equilibrium constant, denoted by K, is a numerical value that expresses the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium. Its value indicates the extent to which a reaction proceeds to completion. A large value of K indicates that the products are favored at equilibrium, while a small value indicates that the reactants are favored. The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo can be used to calculate the equilibrium constant for various reactions and observe how it changes with concentration adjustments.
Utilizing the Gizmo for Effective Learning
The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo offers a powerful learning tool that can be used in various ways. You can:
- Visualize the concept of equilibrium by observing the changing concentrations of reactants and products over time.
- Test the predictions of Le Chatelier’s principle by changing concentrations and observing the resulting shifts in equilibrium.
- Calculate the equilibrium constant for different reactions and analyze its dependence on concentration.
- Explore the effects of temperature and pressure on equilibrium, broadening your understanding of chemical equilibrium.
Key Insights and Tips for Mastering Equilibrium
The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo provides valuable insights for mastering equilibrium. Here are some key takeaways:
- Equilibrium is dynamic: It involves a constant interplay between forward and reverse reactions.
- Concentration plays a crucial role in determining the position of equilibrium.
- Le Chatelier’s principle is a powerful tool for predicting the direction of equilibrium shifts due to concentration changes.
- The equilibrium constant (K) quantifies the extent of a reaction and helps determine which side of the equilibrium is favored.
Expert Advice
To maximize your understanding of equilibrium and concentration, engage with the gizmo actively. Experiment with different scenarios, adjust concentrations, and analyze the resulting changes in equilibrium. Don’t be afraid to explore and challenge your understanding of this fundamental concept. Remember, practice makes perfect!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a reversible reaction and an irreversible reaction?
A reversible reaction is a reaction that can proceed in both forward and reverse directions, while an irreversible reaction proceeds only in one direction. Equilibrium is only possible in reversible reactions.
How does temperature affect equilibrium?
Temperature changes can affect the equilibrium constant (K). Generally, increasing the temperature favors the endothermic reaction, while decreasing the temperature favors the exothermic reaction.
Can you give an example of how Le Chatelier’s principle works?
Consider the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia: N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g). If the concentration of ammonia (NH3) is increased, the equilibrium will shift towards the reactants (N2 and H2) to reduce the excess ammonia.
Equilibrium And Concentration Gizmo Answer Key
Conclusion
The Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo is an invaluable tool for understanding the intricate relationship between concentration and chemical equilibrium. By providing a virtual laboratory for experimentation and observation, it allows you to visualize the dynamic interplay between forward and reverse reactions, test the predictions of Le Chatelier’s principle, and calculate the equilibrium constant. Remember, mastering the concept of equilibrium is essential for understanding the behavior of chemical reactions, and the Equilibrium and Concentration gizmo can help you achieve this goal. Are you interested in exploring more advanced concepts related to equilibrium, such as the impact of temperature and pressure on equilibrium or the relationship between equilibrium constants and Gibbs free energy?






