Have you ever wondered how electricity flows through circuits? What determines the strength of an electrical current? Or how much power a device consumes? The answers to these questions lie in a fundamental law of electricity known as Ohm’s Law. It’s the bedrock of understanding electrical circuits and forms the basis for many practical applications. In this detailed guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of Ohm’s Law, providing you with a solid foundation, practice worksheets with answers, and valuable insights for tackling electrical engineering problems.
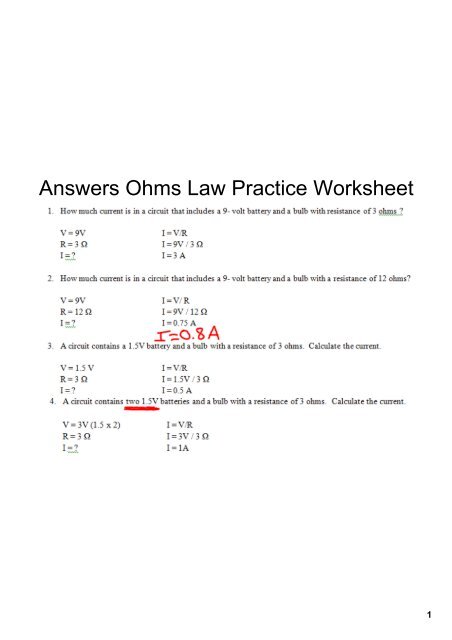
Image: lessonfullandrew.z13.web.core.windows.net
Ohm’s Law, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It’s a simple yet powerful tool that allows us to predict and control electrical behavior. By understanding this law, we can analyze complex circuits, troubleshoot electrical issues, and design efficient electronic devices. Let’s embark on a journey to unlock the secrets of Ohm’s Law and equip ourselves with the knowledge to apply it confidently.
Getting to Know Ohm’s Law: The Fundamentals
Imagine a river flowing downhill. The water’s speed (current) depends on the steepness of the hill (voltage) and the obstacles it encounters (resistance). This analogy perfectly encapsulates the core concepts of Ohm’s Law. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- Voltage (V): Think of voltage as the electrical pressure that drives the flow of current. It’s measured in volts (V). The higher the voltage, the stronger the push for current.
- Current (I): Current represents the rate of flow of electrical charge, measured in amperes (A). It’s analogous to the volume of water flowing in our river analogy. The higher the current, the more charge flows through the circuit.
- Resistance (R): Resistance acts as an obstacle to current flow, impeding its path. It’s measured in ohms (Ω). The higher the resistance, the more it restricts the current.
Ohm’s Law Equation: A Simple Relationship
Ohm’s Law is beautifully expressed in a simple equation:
*V = I R**
This equation tells us that the voltage across a component is directly proportional to the current flowing through it and the resistance of that component.
- V: Voltage (volts)
- I: Current (amperes)
- R: Resistance (ohms)
This equation can be rearranged to solve for any of the three variables:
- I = V / R (current equals voltage divided by resistance)
- R = V / I (resistance equals voltage divided by current)
Practical Applications of Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law isn’t just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples:
- Designing Electrical Circuits: Engineers use Ohm’s Law to calculate the required resistance values for resistors, ensuring proper current flow through components. This is crucial for preventing damage to delicate components and ensuring optimal performance.
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: If a circuit isn’t functioning as expected, Ohm’s Law helps diagnose the issue. By measuring voltage and current, technicians can identify faults like a broken wire, a faulty component, or a short circuit.
- Power Consumption Calculations: The power (P) consumed by an electrical device is calculated using the formula P = V * I, where V is the voltage and I is the current. This allows us to determine the wattage of appliances and compare their energy efficiency.

Image: davida.davivienda.com
Ohm’s Law Worksheets with Answers: Putting Theory into Practice
Now that we understand the fundamentals of Ohm’s Law, let’s dive into some practice problems to solidify our understanding:
Worksheet 1: Simple Circuits
-
A circuit has a voltage of 12V and a resistance of 4Ω. What is the current flowing through the circuit?
-
A device draws a current of 2A when connected to a 120V power source. What is the resistance of the device?
-
A resistor with a resistance of 10Ω has a current of 5A flowing through it. What is the voltage across the resistor?
Answers:
-
I = V/R = 12V / 4Ω = 3A The current flowing through the circuit is 3A.
-
R = V/I = 120V / 2A = 60Ω The resistance of the device is 60Ω.
-
V = I R = 5A 10Ω = 50V The voltage across the resistor is 50V.
Worksheet 2: Complex Circuits
-
A circuit contains two resistors connected in series. The first resistor has a value of 10Ω, and the second resistor has a value of 20Ω. If the voltage across the entire circuit is 30V, what is the current flowing through the circuit?
-
A circuit contains two resistors connected in parallel. The first resistor has a value of 5Ω, and the second resistor has a value of 10Ω. If the voltage across the circuit is 15V, what is the total current flowing through the circuit?
Answers:
-
Total Resistance (R) = 10Ω + 20Ω = 30Ω
Current (I) = V/R = 30V / 30Ω = 1A The current flowing through the circuit is 1A.
-
*Resistance of Parallel Resistors (R) = (5Ω 10Ω) / (5Ω + 10Ω) = 3.33Ω**
Current (I) = V/R = 15V / 3.33Ω = 4.5A The total current flowing through the circuit is 4.5A.
Worksheet 3: Real-World Applications
-
A light bulb has a power rating of 100W and operates on a 120V power source. What is the current flowing through the light bulb?
-
A toaster operates on a 120V power source and has a resistance of 15Ω. What is the power consumption of the toaster?
Answers:
-
*P = V I** The power (P) is 100W and the voltage (V) is 120V.
I = P/V = 100W / 120V = 0.83A The current flowing through the light bulb is 0.83A.
-
P = V² / R = (120V)² / 15Ω = 960W The power consumption of the toaster is 960W.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
- Focus on the Units: Ensuring you’re working with consistent units (Volts, Amps, Ohms) is crucial for accurate calculations.
- Visualize the Circuit: Drawing a simple circuit diagram helps understand the arrangement of components and simplifies calculations.
- Use Ohm’s Law as a Foundation: It’s the cornerstone of electrical analysis; learn to apply it to various scenarios.
- Practice Makes Perfect: The more practice problems you solve, the more confident you’ll become in understanding and applying Ohm’s Law.
Ohm’S Law Worksheet With Answers Pdf
Conclusion: Embark on Your Electrical Journey
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental law in electricity, providing the key to understanding how circuits work. By mastering this law through practice and application, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of electrical engineering and equip yourself with valuable tools to solve problems and innovate. You can download free Ohm’s Law worksheets with answers online to further enhance your comprehension and sharpen your skills. So, embark on this exciting journey to master Ohm’s Law and unlock the hidden world of electricity!






