Ever wondered how your home’s electrical system manages to power multiple appliances simultaneously? Or how a Christmas tree lights up with diverse colors and patterns? The answer lies in a fundamental concept in electronics – the parallel circuit. This ingenious design allows electricity to flow through multiple paths, creating a network of power that can be customized and adapted to various needs.
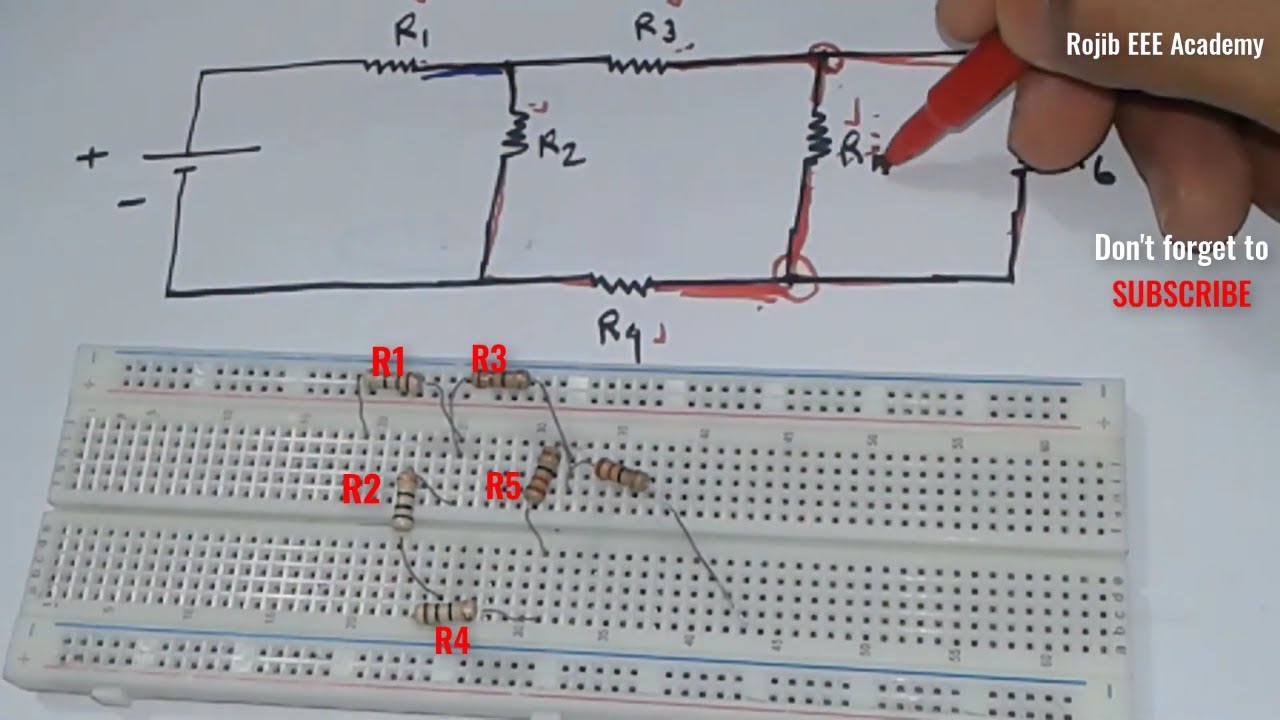
Image: schematiclibrarynathan.z21.web.core.windows.net
In essence, a parallel circuit is an arrangement of electrical components where each component is connected directly to the power source, forming independent pathways for electricity to flow. The result? Multiple devices can operate independently, drawing power directly from the source, offering flexibility and reliability in electrical systems.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Series vs. Parallel
Before diving into the practicalities of building a parallel circuit, let’s first draw a clear distinction between a parallel circuit and its counterpart, the series circuit. Think of them as two different ways to connect electrical components.
In a series circuit, components are connected in a single, unbroken path – a chain. The current flows through each component one after the other. This arrangement is simple, but it has limitations. If one component fails, the entire circuit breaks, and the flow of current stops. Imagine a string of Christmas lights – if a single bulb burns out, the whole string goes dark.
Conversely, a parallel circuit provides multiple pathways for current to flow. Imagine individual branches branching off from a main road. Each component has its own dedicated path, so if one component fails, the others remain unaffected. Returning to the Christmas lights example, if a bulb burns out in a parallel circuit, the other lights stay illuminated.
Building a Parallel Circuit: A Step-by-Step Guide
Building a parallel circuit is a straightforward process requiring basic components and a little bit of understanding. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
1. Gather the Essential Components
- Power Source: This can be a battery, a power supply, or even a wall outlet.
- Resistors: Resistors limit the flow of current. You’ll need one resistor for each component in your circuit.
- Components: These could be LEDs, motors, buzzers, or any electrical device you want to connect in parallel.
- Wires: These will connect the components to the power source and to each other.
- Soldering Iron (optional): For a more permanent connection, you can use a soldering iron to solder the wires to the components.
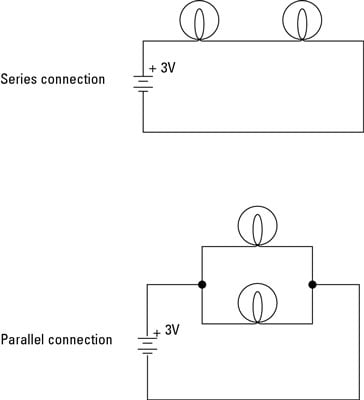
Image: www.176iot.com
2. The Circuit Design
- Start with the power source. Connect one end of your power source to the first component.
- Connect the first component to the second component. These connections should be made in separate, parallel branches.
- Repeat the process for each component. Each component should be connected directly to the power source, forming a separate path.
- Connect the other end of the power source to the other end of your last component. This completes the circuit.
3. Connecting the Components
Here’s how to connect the components together in a parallel circuit, ensuring each component has its own dedicated path:
- Connect a wire from the positive terminal of the power source to one leg of the first resistor.
- Connect a wire from the other leg of the first resistor to one leg of the first component.
- Connect another wire from the other leg of the first component directly back to the positive terminal of the power source.
- Repeat these steps for each additional component, ensuring each has its own independent path to the power source.
4. Closing the Circuit
Finally, connect a wire from the negative terminal of the power source to each of the components’ other legs. This completes the parallel circuit, allowing the current to flow through each component independently.
Real-World Applications: Where Parallel Circuits Shine
Parallel circuits are the backbone of modern electronics, powering countless devices and systems. Their ability to provide independent pathways for electricity has made them indispensable in various applications:
- Home Electrical Systems: Each outlet in your home is connected in parallel, allowing you to plug in and use multiple appliances without interfering with each other’s functionality.
- Automotive Wiring: The various electrical components in a vehicle, like headlights, taillights, and dashboard lights, are all connected in parallel.
- Computer Systems: Multiple components in a computer, such as the CPU, RAM, and hard drive, are powered in parallel, ensuring each component receives the necessary electricity to operate.
- Christmas Tree Lights: You’ve already heard this example, but it bears repeating. Stringing lights in parallel ensures that if one bulb burns out, the entire string stays lit.
Parallel Circuits and Voltage
One of the key advantages of parallel circuits is that each component in the circuit experiences the same voltage as the power source. This means that even though the current flowing through each component might be different, the voltage across each component will be identical.
For example, if you have a 12-volt battery connected to a parallel circuit with three resistors, each resistor will have 12 volts across it. This makes parallel circuits ideal for applications where all components need to operate at the same voltage.
Safety Precautions: Working with Electricity
While building parallel circuits can be a fun and educational endeavor, it’s crucial to remember the inherent dangers of working with electricity. Always ensure the voltage being used is safe and appropriate for the components involved. Use caution and follow these safety guidelines:
- Never work with high voltage circuits unless you have the proper training and experience.
- Always disconnect the power source before making any changes to the circuit.
- Use insulated tools and handle wires carefully.
- Never touch exposed wires or components while the circuit is live.
- **If you are unsure about anything, consult a qualified electrician.
How To Build A Parallel Circuit
https://youtube.com/watch?v=zrJNRj9g5kU
Conclusion: Unveiling the Power of Parallel Circuits
Building a parallel circuit is an engaging process that unveils the fascinating workings of electrical systems. By understanding the fundamentals, you can unlock the power of multiple paths, creating flexible and efficient circuits that drive diverse applications. From your home’s wiring to the intricate systems that power your electronic devices, parallel circuits are the unsung heroes of modern electrical engineering. Explore further, experiment, and discover the endless possibilities of these versatile circuits!






