Have you ever wondered if your blood type could influence your health and wellbeing? You’re not alone. Many people are intrigued by the concept of “eat right 4 your blood type,” a popular dietary theory that suggests tailoring your diet based on your blood group. While the idea may sound appealing, the reality is more complex. This article will delve into the scientific evidence and explore the validity of this popular health trend.
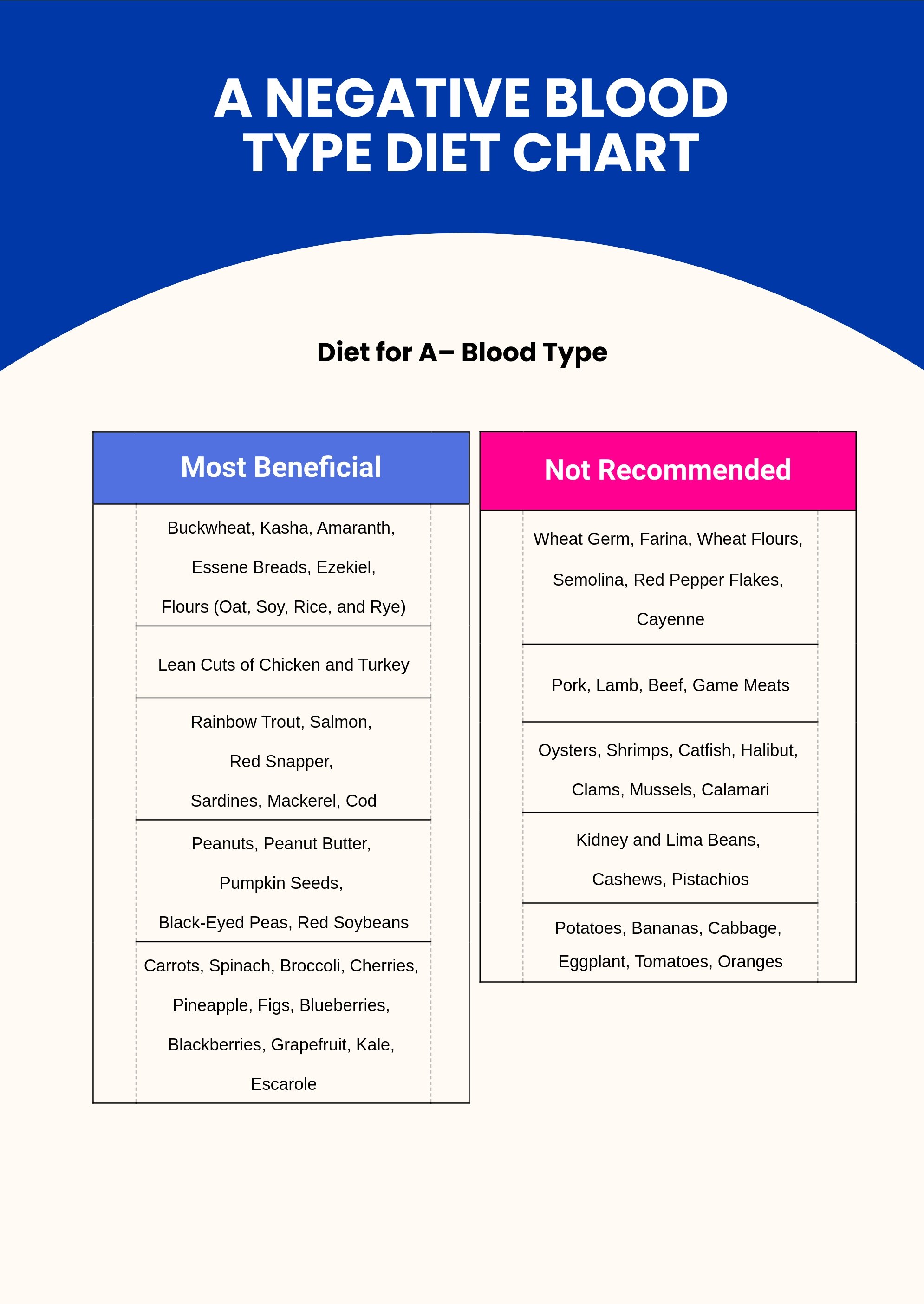
Image: www.template.net
The “eat right 4 your blood type” concept, also known as the “blood type diet,” originated from the writings of Dr. Peter J. D’Adamo, a naturopathic physician. The theory proposes that specific foods can either promote or impede digestion and health depending on your blood type. It claims that blood types evolved differently over time and are associated with specific immune responses and digestive capabilities, dictating dietary needs. While the idea has gained traction, the scientific community remains largely skeptical about its effectiveness.
The Blood Type Diet: A Closer Look
The Basics of Blood Types
Before diving into the blood type diet, let’s understand the basics of blood types. Humans have four main blood types: A, B, AB, and O. These types are determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens, which are protein markers found on the surface of red blood cells. The immune system recognizes these antigens, and incompatible blood types can lead to immune reactions.
The Premise of the Blood Type Diet
The blood type diet argues that blood types have an impact beyond blood transfusions, influencing everything from metabolism to immunity. Dr. D’Adamo’s theory suggests that individuals with different blood types produce different lectins, proteins that can bind to cells and potentially influence digestion, inflammation, and other bodily processes.

Image: www.aiophotoz.com
Suggested Dietary Guidelines
Each blood type, according to the theory, has a specific recommended diet:
- Blood Type A: Primarily vegetarian, focusing on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting red meats and dairy products.
- Blood Type B: More flexible, allowing for a variety of foods including meats, dairy, and grains, with an emphasis on green leafy vegetables.
- Blood Type AB: Described as a combination of A and B, suggesting a balanced diet with both meat and vegetarian options.
- Blood Type O: Promoted as the “hunter-gatherer” type, emphasizing meat, fish, and vegetables, with limited grains and dairy.
The Scientific Evidence: A Critical Evaluation
Lack of Robust Scientific Support
Despite its popularity, the blood type diet lacks robust scientific evidence to support its claims. Numerous studies have been conducted, yet their results have been mixed, with some suggesting a weak correlation while others finding no significant connection between blood type and dietary needs.
Concerns and Limitations
Several limitations hinder the validity of the blood type diet:
- Small Sample Sizes: Many studies have involved small sample sizes, which may not be representative of the general population.
- Lack of Long-Term Studies: Most research has focused on short-term effects, leaving unanswered questions about long-term health outcomes.
- Oversimplification of Complex Processes: The theory oversimplifies complex biological processes, ignoring genetic diversity and individual differences.
- Potential Bias: The proponents of the diet may have inherent biases that influence research findings.
The Importance of Personalized Nutrition
A growing body of evidence points to the importance of personalized nutrition. This approach recognizes that each individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health history contribute uniquely to their health needs. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition, and focusing on individual factors is crucial for optimal health.
Beyond the Blood Type Diet: A Holistic Approach
Focus on a Balanced Diet
Rather than relying on blood type-specific dietary guidelines, it’s more sensible to adopt a well-balanced and nutritious diet that meets your individual needs. This includes:
- Plenty of fruits and vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
- Lean proteins: Essential for building and repairing tissues.
- Whole grains: Provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients.
- Healthy fats: Crucial for hormone production and cell function.
Consider Individual Factors
A personalized approach to nutrition considers your specific needs, preferences, and health goals. Consulting with a registered dietitian or another qualified healthcare professional can provide tailored guidance for meal planning and dietary choices.
Eat Right 4 Your Health: A Practical Guide
The Importance of Evidence-Based Information
When it comes to your health and nutrition, it’s crucial to rely on evidence-based information from reputable sources. Avoid falling prey to diet trends or claims that lack scientific backing.
Understanding Your Body
Pay attention to your body’s signals. Notice how different foods affect your energy levels, digestive system, and overall well-being. This self-awareness can help you identify dietary patterns that are best suited for you.
Making Gradual Changes
Don’t try to overhaul your diet overnight. Make gradual changes, gradually incorporating new foods and healthy habits into your routine. This approach makes it easier to stick with changes in the long run.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or a physician, can provide personalized guidance and ensure you make informed choices about your nutrition.
Eat Right 4 Your Blood Type Pdf
Conclusion
The “eat right 4 your blood type” diet, while intriguing, lacks sufficient scientific evidence to support its claims. Instead of relying on these unproven theories, focus on a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that considers your individual needs. Remember, a healthy lifestyle goes beyond just what you eat, encompassing regular exercise, adequate sleep, and managing stress. Embrace evidence-based information, consult healthcare professionals, and prioritize your overall health and well-being.






